Digital Image Processing System
In computer science, digital image processing uses algorithms to perform image processing on digital images to extract some useful information. Digital image processing has many advantages as compared to analog image processing. Wide range of algorithms can be applied to input data which can avoid problems such as noise and signal distortion during processing. As we know, images are defined in two dimensions, so DIP can be modeled in multidimensional systems.
Purpose of Image processing
The main purpose of the DIP is divided into following 5 groups:
- Visualization: The objects which are not visible, they are observed.
- Image sharpening and restoration: It is used for better image resolution.
- Image retrieval: An image of interest can be seen
- Measurement of pattern: In an image, all the objects are measured.
- Image Recognition: Each object in an image can be distinguished.
Following are Fundamental Steps of Digital Image Processing:
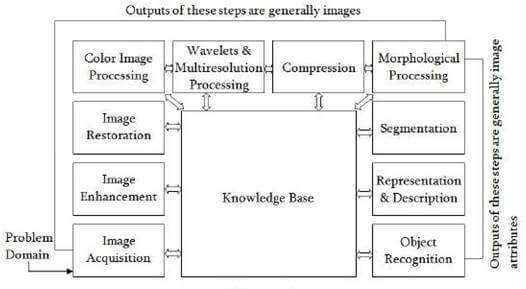
1. Image Acquisition
Image acquisition is the first step of the fundamental steps of DIP. In this stage, an image is given in the digital form. Generally, in this stage, pre-processing such as scaling is done.
2. Image Enhancement
Image enhancement is the simplest and most attractive area of DIP. In this stage details which are not known, or we can say that interesting features of an image is highlighted. Such as brightness, contrast, etc...
3. Image Restoration
Image restoration is the stage in which the appearance of an image is improved.
4. Color Image Processing
Color image processing is a famous area because it has increased the use of digital images on the internet. This includes color modeling, processing in a digital domain, etc....
5. Wavelets and Multi-Resolution Processing
In this stage, an image is represented in various degrees of resolution. Image is divided into smaller regions for data compression and for the pyramidal representation.
6. Compression
Compression is a technique which is used for reducing the requirement of storing an image. It is a very important stage because it is very necessary to compress data for internet use.
7. Morphological Processing
This stage deals with tools which are used for extracting the components of the image, which is useful in the representation and description of shape.
8. Segmentation
In this stage, an image is a partitioned into its objects. Segmentation is the most difficult tasks in DIP. It is a process which takes a lot of time for the successful solution of imaging problems which requires objects to identify individually.
9. Representation and Description
Representation and description follow the output of the segmentation stage. The output is a raw pixel data which has all points of the region itself. To transform the raw data, representation is the only solution. Whereas description is used for extracting information's to differentiate one class of objects from another.
10. Object recognition
In this stage, the label is assigned to the object, which is based on descriptors.
11. Knowledge Base
Knowledge is the last stage in DIP. In this stage, important information of the image is located, which limits the searching processes. The knowledge base is very complex when the image database has a high-resolution satellite.
.png)

